India Signals Deep Tech Growth with New Startup Rules 2026
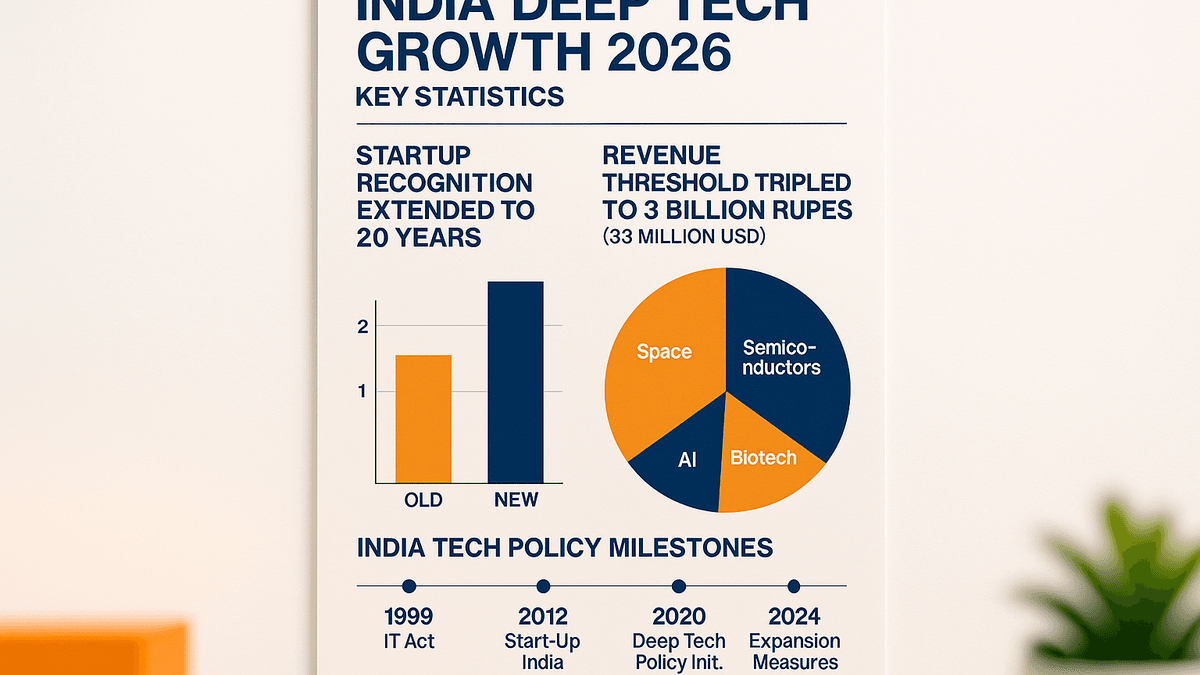
India updates its startup framework to support deep tech sectors, extending the startup recognition period to 20 years and increasing the revenue threshold for benefits.
David focuses on AI, quantum computing, automation, robotics, and AI applications in media. Expert in next-generation computing technologies.
LONDON, February 8, 2026 — India has announced a significant shift in its startup framework to support deep tech sectors, such as space, semiconductors, and biotech. According to TechCrunch, the Indian government has extended the period for which deep tech companies are considered startups to 20 years, and increased the revenue threshold for startup-specific benefits to ₹3 billion ($33.12 million) from ₹1 billion ($11.04 million).
Executive Summary
- India updates its startup rules to better accommodate deep tech sectors.
- The startup recognition period is extended from 10 to 20 years.
- The revenue threshold for tax benefits is tripled to ₹3 billion ($33.12 million).
- The changes align with the long development cycles of deep tech industries including space, semiconductors, and biotech.
- India positions itself alongside the US, China, and the EU in the global deep tech race.
Key Developments
India's decision to modify its startup ecosystem rules is a strategic move to bolster deep tech innovation. For more on related AI developments. With sectors like space, semiconductors, and biotech often requiring extended development timelines, the government's initiative to double the startup recognition period to 20 years is a crucial adjustment. This change allows these startups to benefit from tax, grant, and regulatory incentives for a longer duration, aligning with their unique business cycles. Additionally, the revenue threshold for accessing these benefits has been increased to ₹3 billion, tripling the previous limit, to better support companies as they grow and scale.
The government's mobilization of public capital aims to facilitate the journey of deep tech firms from concept to commercialization, a path known for its complexity and resource-intensive nature. According to Reuters, India's deep tech sector attracted over $3.6 billion in venture capital funding in 2025, a figure expected to grow substantially under the revised framework.
India Deep Tech Policy: Before vs After
| Parameter | Previous Rules | New Rules (2026) | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Startup Recognition Period | 10 years | 20 years | +100% |
| Revenue Threshold | ₹1 billion ($11M) | ₹3 billion ($33M) | +200% |
| Tax Holiday Eligibility | 3 of first 10 years | 5 of first 20 years | Extended |
| Sectors Covered | General tech startups | Deep tech priority (Space, Semi, Biotech, AI) | Targeted |
| Public Capital Mobilization | Limited | Dedicated deep tech fund | New |
Market Context
The deep tech sector, encompassing industries like space exploration, semiconductor fabrication, and biotechnology, is characterized by its reliance on cutting-edge scientific and engineering advancements. Unlike more traditional tech startups, deep tech companies face extended timelines due to the intricate nature of research, development, and regulatory approvals. In recent years, there has been a global trend towards supporting these sectors as they hold the potential to drive significant technological and economic advancements.
Countries like the United States and China have also been active in adjusting their policies to foster growth in these industries. The US CHIPS and Science Act allocated $52.7 billion for semiconductor manufacturing, while China's "Made in China 2025" programme has directed hundreds of billions into deep tech sectors. India's new rules reflect an understanding of these global dynamics and a commitment to positioning itself as a serious competitor in deep tech innovation.
Global Deep Tech Investment Comparison (2025-2026)
| Country/Region | Key Policy | Deep Tech VC Funding (2025) | Focus Sectors |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | CHIPS Act ($52.7B) | $48.2 billion | Semiconductors, AI, Quantum |
| China | Made in China 2025 | $38.5 billion | Semiconductors, Biotech, Space |
| European Union | EU Chips Act (€43B) | $22.1 billion | Semiconductors, Clean Tech |
| India | Deep Tech Startup Rules 2026 | $3.6 billion | Space, Semiconductors, Biotech, AI |
| South Korea | K-Semiconductor Strategy | $8.9 billion | Semiconductors, Display Tech |
| Japan | Semiconductor Revival Plan | $6.3 billion | Semiconductors, Robotics |
Source: Bloomberg, Financial Times, NASSCOM estimates (2025-2026)
India Deep Tech Growth Data
BUSINESS 2.0 Analysis
India's revised startup regulations represent an astute recognition of the unique needs of deep tech industries. For more on related AI developments. By extending the startup designation to 20 years, the government acknowledges the protracted timelines necessary for deep tech companies to navigate R&D phases and achieve commercial viability. This policy shift could catalyse a surge in deep tech entrepreneurship, attracting both domestic and international investors who may have previously hesitated due to the shorter policy windows.
Furthermore, increasing the revenue threshold to ₹3 billion reflects an understanding of the substantial capital requirements typical of these industries. This move could enhance the competitive landscape in India, encouraging startups to pursue ambitious projects without the immediate pressure of financial constraints. The mobilization of public capital as part of this initiative also signals a commitment to overcoming funding gaps that traditionally hinder deep tech startups.
"India's updated deep tech framework addresses a critical gap in how emerging economies nurture capital-intensive innovation," said Mohandas Pai, Chairman of Manipal Global Education, in an interview with Mint. "The 20-year recognition window gives founders the runway they actually need."
As India positions itself on the global stage, these regulatory changes could pave the way for significant breakthroughs in technology and innovation, particularly in semiconductor fabrication where the country is investing $10 billion through the India Semiconductor Mission.
Why This Matters for Industry Stakeholders
For industry stakeholders, particularly investors and entrepreneurs, India's updated rules offer both opportunities and challenges. The extended startup recognition period and increased revenue threshold create a more favourable environment for long-term investment in deep tech sectors. Investors can commit resources with greater confidence, knowing there is ample time for startups to mature and yield returns.
"The tripling of the revenue threshold is perhaps more significant than the timeline extension," noted Rajan Anandan, Managing Director at Sequoia Capital India, speaking to The Economic Times. "It means deep tech companies can scale to meaningful revenue without losing their startup benefits."
For entrepreneurs, these changes reduce the pressure to achieve rapid financial milestones, allowing a focus on innovation and product development. However, stakeholders must also navigate the complexities of a shifting regulatory landscape and ensure alignment with the new policies to maximise benefits.
Forward Outlook
Looking ahead, India's regulatory adjustments are likely to stimulate growth in the deep tech sector, positioning the country as a competitive player in the global technology landscape. For more on related AI developments. The changes may attract a wave of new startups and investors seeking to leverage the extended support framework.
However, the success of these initiatives will depend on effective implementation and the ability to maintain a supportive ecosystem for innovation. As deep tech industries advance, there will be a continued need for collaboration between government, industry, and academia to address challenges such as talent development, infrastructure, and market access. By fostering an environment conducive to deep tech innovation, India could potentially lead in areas such as space exploration, semiconductor manufacturing, and biotechnology by 2030.
Disclosure: This analysis reflects publicly available policy announcements and market data. Forward-looking statements are based on current trends and are subject to change. BUSINESS 2.0 NEWS maintains editorial independence.
Key Takeaways
- India extends deep tech startup designation to 20 years, aligning with industry timelines.
- Revenue threshold for startup benefits increased to ₹3 billion ($33.12 million), tripling the previous limit.
- Public capital mobilisation aims to support commercialisation of deep tech innovations.
- India's $3.6 billion deep tech VC funding in 2025 is expected to grow substantially under the new framework.
- Regulatory changes position India alongside the US, China, and the EU in the global deep tech competition.
References
About the Author
David Kim
AI & Quantum Computing Editor
David focuses on AI, quantum computing, automation, robotics, and AI applications in media. Expert in next-generation computing technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What changes has India made to its startup rules?
India has extended the startup recognition period for deep tech companies to 20 years and increased the revenue threshold for startup-specific benefits to ₹3 billion. This shift aims to accommodate the long development cycles typical of deep tech industries, such as space and biotechnology, allowing these companies to benefit from tax, grant, and regulatory incentives for a longer period. (Source: TechCrunch)
How will these changes impact the market?
The updated rules are expected to stimulate growth in India's deep tech sector by creating a more favorable environment for long-term investment and development. The extended support period and higher revenue threshold may attract more investors and startups to India, enhancing the country's global competitiveness in emerging technology sectors. (Source: Business 2.0 Analysis)
What are the implications for investors?
Investors can now approach the Indian deep tech market with greater confidence, as the extended startup recognition period and increased revenue threshold reduce risk and provide more time for startups to mature. This creates opportunities for long-term investments in sectors that traditionally face high initial capital requirements and extended development timelines. (Source: Business 2.0 Analysis)
What technical factors are considered in these changes?
The changes account for the unique technical challenges faced by deep tech startups, such as prolonged R&D phases and the need for substantial capital investment. By extending the timeline and increasing the revenue threshold, the Indian government aims to align policy with the technical realities of these industries, supporting innovation and development. (Source: TechCrunch)
What is the future outlook for India's deep tech sector?
India's regulatory adjustments are likely to position the country as a leader in the global deep tech landscape. The changes may attract new startups and investors, fostering innovation and technological advancement. Continued collaboration between government, industry, and academia will be crucial to addressing challenges and maximizing the potential of these initiatives by 2030. (Source: Business 2.0 Analysis)
